
or, the phrase samplers including Groove machines, etc.Īlternative subsets of audio sequencers include: Audio data on the audio sequencers including DAW, loop-based music software, etc.
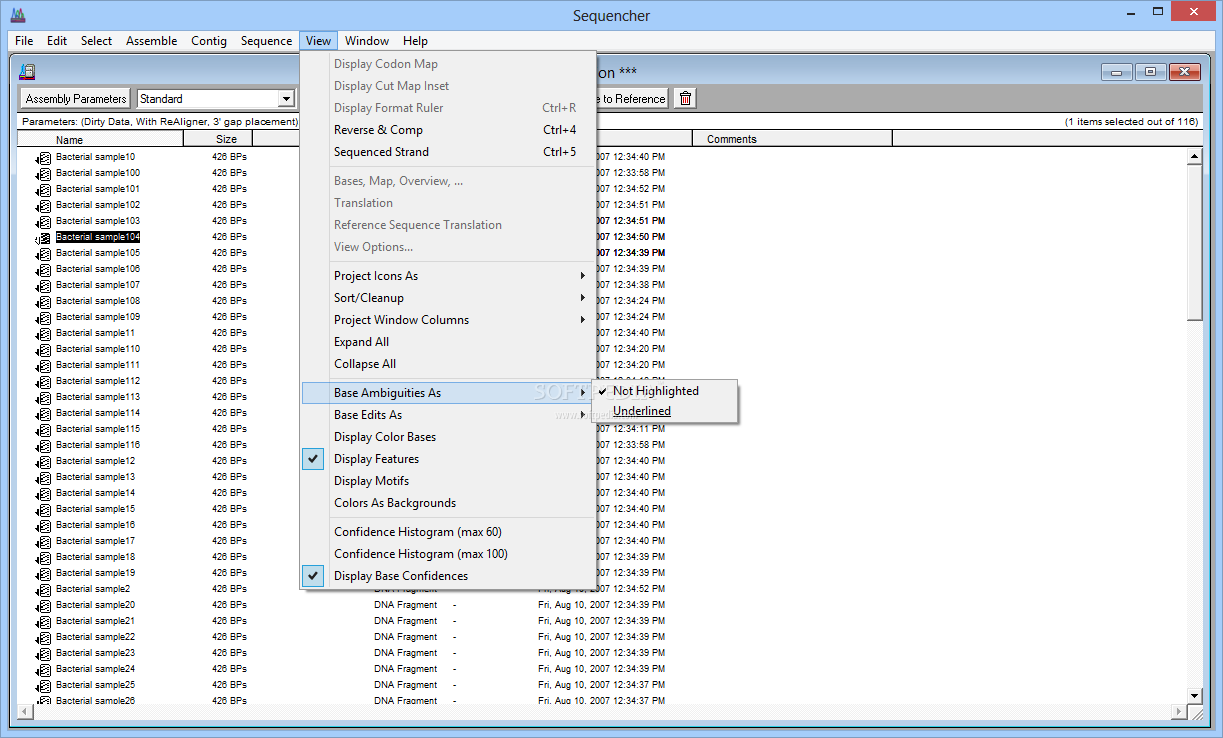
#SEQUENCHER SOFTWARE#
Automation data for mixing-automation on the DAWs, and the software effect / instrument plug-ins on the DAWs with sequencing features.CV/Gate data on the analog sequencers and possibly others (via CV/Gate interfaces).
These new sequencers could also be used to control external synthesizers, especially rackmounted sound modules, and it was no longer necessary for each synthesizer to have its own devoted keyboard.Īs the technology matured, sequencers gained more features, such as the ability to record multitrack audio. Software-based sequencers allowed musicians to program performances that were more expressive and more human. This software also improved on the quality of the earlier sequencers which tended to be mechanical sounding and were only able to play back notes of exactly equal duration. The advent of Musical Instrument Digital Interface (MIDI) and the Atari ST home computer in the 1980s gave programmers the opportunity to design software that could more easily record and play back sequences of notes played or programmed by a musician. See also: § Software sequencers, Audio sequencer, Digital audio workstation, and Audio plug-in


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
